
January 24th, 2017 by Elma Jane
How to set up a travel merchant account?
First, you need to find a Merchant Service Provider.
Put together your business profile so you can start applying for a merchant account.
There are questions that you’ll need to answer, that way merchant account providers have an idea of how they should set up your account.
Some of the questions are:
Is your business seasonal?
For Travel Agencies or Tour Operators, it is seasonal, there will be high and low volume. NTC works with seasonal downtime.
How do you intend to accept payments?
Different business models require different methods of accepting payments.
If you’re doing face to face transaction and have a physical location then you need a credit card terminal.
If you process checks, then you need Electronic Check and ACH Transfers.
For e-Commerce shopping carts, wireless/mobile, you can check out our Converge Virtual Merchant and NTC e-Pay.
How much volume do you plan on processing?
Merchant account providers are going to want to know how much sales volume you plan on processing per month.
If you’re new in the business – give just an estimate average of how much you’ll be processing (per month), within the first 6-months of operation.
if you’ve been in the business – you’ll already have this number ready.
What will be your average ticket price?
Example:
Total Sales Revenue = $150,000
Total Number of Sales = 500 150,000/500 = $300 (Average Ticket Price)
If you need to setup an account give us a call at 888-996-2273 or use our contact form.
Posted in Best Practices for Merchants Tagged with: ach, credit card, e-commerce, E-Pay, Electronic Check, merchant account, merchant service provider, mobile, payments, shopping carts, terminal, transaction, travel, virtual merchant
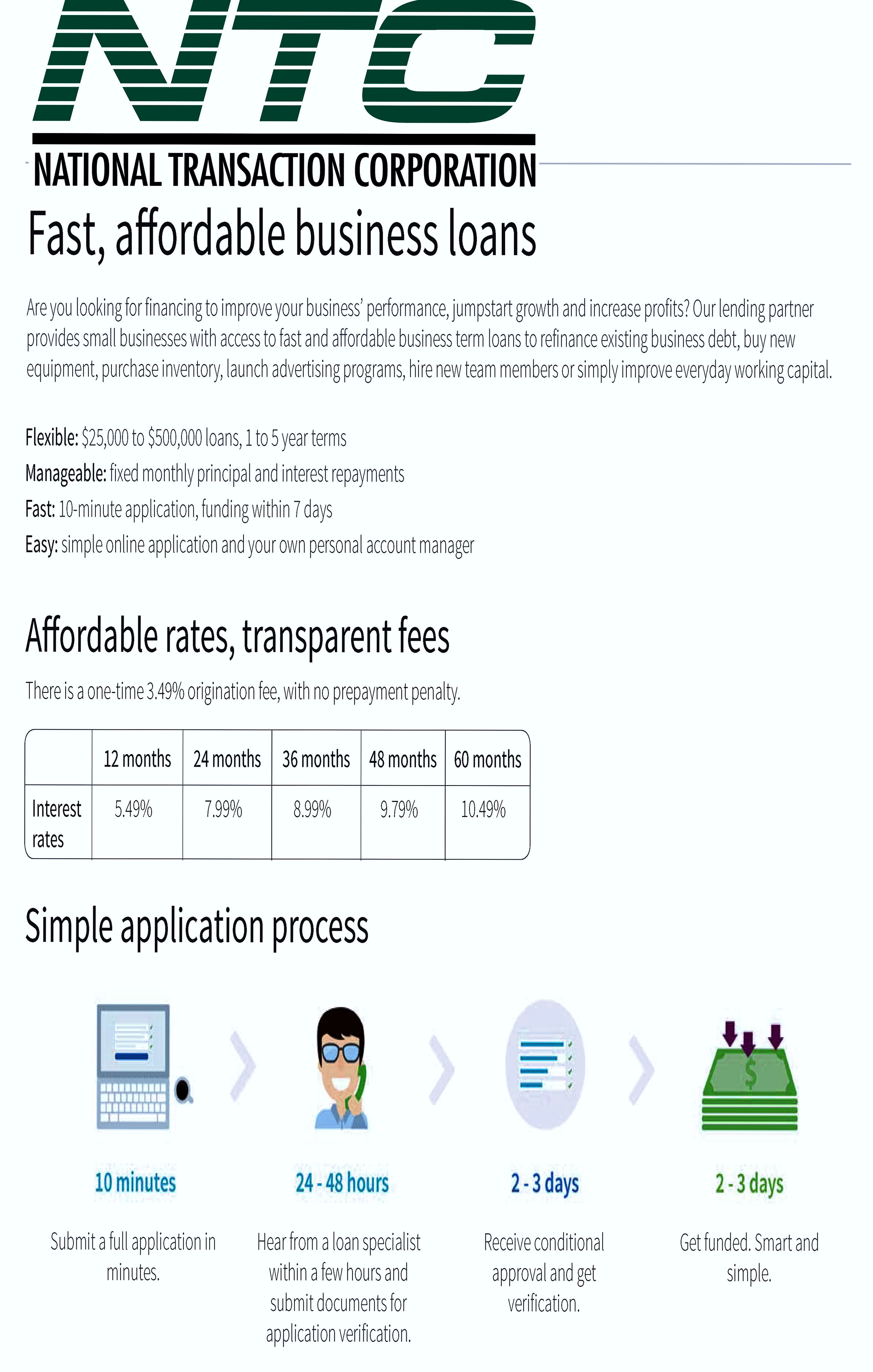
July 19th, 2016 by Elma Jane
Here are some of the Common Business Loan Fees:
Application Fee – is a fee charged to cover the costs of processing and assessing your loan application.
Bank Wire Fee – When borrowing a loan, lenders commonly wire the money to your bank account via ACH, because the banks need to talk to each other and ensure the money is going to the right place and that no fraud is going on.
Check Processing Fee – ACH transfers are commonly used to collect periodic repayments from the debtor’s bank account. Some lenders offer the option of paying by check, but you’ll have to pay a fee for the extra cost involved.
Closing Cost – not to be confused with closing fees, encapsulate all the fees charged for processing a loan, including origination/closing fees, processing fees, referral fees, and/or packaging fees.
Draw Fee – similar to an origination fee, but is applicable instead for lines of credit.
Guarantee Fee – is charged on all SBA loans above $150K. Guarantee fee is charged to protect against credit-related losses in the mortgage portfolio.
Late Payment Fee – Missing a payment deadline can result in a late fee. A late payment may have an affect on your personal or business credit score.
Origination Fee – an up-front fee charged for processing a new loan application. Prepayment
Penalty – Is a borrower, a bank or mortgage lender agreement that regulates what the borrower is allowed to pay off and when.
Servicing and Maintenance Cost – fees charged to cover the costs associated with collecting payments, maintaining records, following up on delinquencies and any other costs associated with maintaining a term loan or line of credit.
Business loans are available in different types, from merchant cash advances to lines of credit. The most effective way to get the best deal on a business loan is to be educated and know that Fees are Negotiable.
Posted in Best Practices for Merchants, Financial Services Tagged with: ach, bank account, check, credit, fee, fraud, loan, payment

October 12th, 2015 by Elma Jane
Setting up a merchant account.
- First find a Merchant Service Provider.
- Then setup your Business Profile.
Put together your business profile so you can start applying for a merchant account. There are questions that you’ll need to answer, that way merchant account providers have an idea of how they should setup your account.
Some of the questions are:
- Is your business seasonal? For Travel Company it is seasonal, there will be high and low volume. NTC works with seasonal downtime.
- How do you intend to accept payments? Different business models require different methods of accepting payments. If you’re doing face to face transaction and have physical location then you need a credit card terminal. If you process checks, then you need Electronic Check and ACH Transfers. For e-Commerce shopping carts, wireless/mobile, you can check out our Converge Virtual Merchant and NTC e-Pay.
- How much volume do you plan on processing? Merchant account providers are going to want to know how much sales volume you plan on processing per month. New in the business – give just an estimate average of how much you’ll be processing (per month), within the first 6-months of operation. Been in the business – you’ll already have this number ready.
- What will be your average ticket price?
Example:
Total Sales Revenue = $150,000
Total Number of Sales = 500 150,000/500 = $300 (Average Ticket Price)
If you need to setup an account give us a call now at 888-996-2273 or go to www.nationaltransaction.com to know more about our services.
Posted in Best Practices for Merchants, e-commerce & m-commerce Tagged with: ach, Converge, credit card terminal, e-commerce, Electronic Check, merchant account, merchant service provider, NTC e-Pay, payments, Travel Company, virtual merchant
April 6th, 2015 by Elma Jane
Merchant Cash Advance – A lump-sum payment to a business in exchange for an agreed-upon percentage of future credit card and/or debit card sales. The term is now commonly used to describe a variety of small business financing options characterized by short payment terms (generally under 24 months) and small regular payments (typically paid each business day) as opposed to the larger monthly payments and longer payment terms associated with traditional bank loans.
Merchant Cash Advance companies, provide funds to businesses in exchange for a percentage of the businesses daily credit card income, directly from the processor that clears and settles the credit card payment. A company’s remittances are drawn from customers’ debit-and credit-card purchases on a daily basis until the obligation has been met. Most providers form partnerships with payment processors and then take a fixed variable percentage of a merchant’s future credit card sales.
The Term Merchant Cash Advance – may be used to describe purchases of future credit card sales receivables, revenue and receivables factoring or short-term business loans.
This structure has some advantage over the structure of a conventional loan. Most importantly, payments to the merchant cash advance company fluctuate directly with the merchant’s sales volumes, giving the merchant greater flexibility with which to manage their cash flow, particularly during a slow season. Advances are processed quicker than a typical type loan, giving borrowers quicker access to capital. Also, because MCA providers like typically give more weight to the underlying performance of a business who may not qualify for a conventional loan.
Merchant Cash Advances are often used by businesses that do not qualify for regular bank loans, and are generally more expensive than bank loans. Competition and innovation led to downward pressure on rates and terms are now more closely correlated with an applicant’s FICO score.
There are generally three different repayment methods:
Split withholding – when the credit card processing company automatically splits the credit card sales between the business and the finance company per the agreed portion. The most common preferred method of collecting funds for both the clients and finance companies since it is seamless.
Lock box or trust bank account withholding – all of the business’s credit card sales are deposited into bank account controlled by the finance company and then the agreed upon portion is forwarded onto the business via ACH, EFT or wire. The least preferred method since it results in a one-day delay in the business receiving the proceeds of their credit card sales.
ACH withholding – when structured as a sale, the finance company receives the credit card processing information and deducts its portion directly from the business’s checking account via ACH. When structured as a loan, the finance company debits a fixed amount daily regardless of business sales.
Posted in Best Practices for Merchants, Financial Services, Merchant Account Services News Articles, Merchant Cash Advance, Merchant Services Account Tagged with: ach, bank loans, business loans, checking account, conventional loan, credit card processing, credit card sales, credit-card, debit card, finance company, loan, MCA providers, merchant, merchant cash advance, payments
March 17th, 2015 by Elma Jane
Merchant Cash Advance – A lump-sum payment to a business in exchange for an agreed-upon percentage of future credit card and/or debit card sales. The term is now commonly used to describe a variety of small business financing options characterized by short payment terms (generally under 24 months) and small regular payments (typically paid each business day) as opposed to the larger monthly payments and longer payment terms associated with traditional bank loans. The term Merchant Cash Advance may be used to describe purchases of future credit card sales receivables, revenue and receivables factoring or short-term business loans.
Merchant Cash Advance companies, provide funds to businesses in exchange for a percentage of the businesses daily credit card income, directly from the processor that clears and settles the credit card payment. A company’s remittances are drawn from customers’ debit-and credit-card purchases on a daily basis until the obligation has been met. Most providers form partnerships with payment processors and then take a fixed variable percentage of a merchant’s future credit card sales.
These Merchant Cash Advances are not loans – rather, they are a sale of a portion of future credit and/or debit card sales.
This structure has some advantage over the structure of a conventional loan. Most importantly, payments to the merchant cash advance company fluctuate directly with the merchant’s sales volumes, giving the merchant greater flexibility with which to manage their cash flow, particularly during a slow season. Advances are processed quicker than a typical type loan, giving borrowers quicker access to capital. Also, because MCA providers like typically give more weight to the underlying performance of a business who may not qualify for a conventional loan.
Merchant Cash Advances are often used by businesses that do not qualify for regular bank loans, and are generally more expensive than bank loans. Competition and innovation led to downward pressure on rates and terms are now more closely correlated with an applicant’s FICO score.
There are generally three different repayment methods:
Split withholding – when the credit card processing company automatically splits the credit card sales between the business and the finance company per the agreed portion. The most common preferred method of collecting funds for both the clients and finance companies since it is seamless.
Lock box or trust bank account withholding – all of the business’s credit card sales are deposited into bank account controlled by the finance company and then the agreed upon portion is forwarded onto the business via ACH, EFT or wire. The least preferred method since it results in a one-day delay in the business receiving the proceeds of their credit card sales.
ACH withholding – when structured as a sale, the finance company receives the credit card processing information and deducts its portion directly from the business’s checking account via ACH. When structured as a loan, the finance company debits a fixed amount daily regardless of business sales.
Posted in Best Practices for Merchants, Merchant Account Services News Articles, Merchant Cash Advance Tagged with: ach, bank loans, business loans, checking account, conventional loan, credit card processing, credit card sales, credit-card, debit card, finance company, loan, MCA providers, merchant, merchant cash advance, payments
April 15th, 2014 by Elma Jane
Amsterdam, Netherlands-based Cardis has been piloting its technology in Europe with Raiffeisen Bank in Austria and Sberbank in Russia. They are now focused on the U.S., as this is the fastest growing mobile payments market in the world, where there’s a huge opportunity. Integration of technology with a large U.S. processor and with a major U.S. retail brand, which will be launching a mobile site and mobile app using Cardis solution.
Cardis International is planning an April launch in the U.S. for its technology, which enables merchants to accept low-value contactless or mobile payments without incurring high processing charges. Cardis is able to bring down the processing cost of low-value payments, the company said, by aggregating multiple transactions into a single payment.
The problem
Contactless card and NFC-based mobile payments are typically for low amounts, and yet still use a card processing infrastructure that was designed 40 years ago when the average credit card transaction was $100.
Traditional card processing systems require each transaction to be individually processed through the payment system, including authorization, clearing and settlement. The resulting variable costs of processing each transaction are independent of the transaction amount and too high for low-value payments, particularly in low-margin industries such as quick-service restaurants. QSR restaurants often have a 3 percent profit margin, yet, for low-value contactless payments, the processing cost could be as high as 6-7 percent of the transaction value.
Mobile and contactless cards offer consumers a convenient form factor. But they don’t solve the problem that low-value card payments are very expensive for merchants.
As an ever-increasing percentage of transactions have become cashless, card processing fees have become a significant cost. Costs that are based on the number of transactions, rather than their value. With average per person expenditures of $5 or under, feels each swipe fee much more than a business where customers spend $50 or more. But not accepting credit/debit cards for low-value transactions isn’t an option as many of customers don’t carry cash anymore.
Aggregation
Cardis’ solution is to act as an aggregator of low-value payments, sending a single batched transaction through to a processor instead of multiple low-value transactions. As there is no per transaction processing of individual low-value purchases, the cost-per-transaction is significantly reduced.
Cardis provides its technology as a software plug-in to payment service providers for contact-based and contactless card payments, mobile wallet transactions and NFC payments.
There are two models. For card payments, it will aggregate multiple purchases by an individual cardholder at a single merchant on a post-paid basis up to a specific amount, for example $20. To guarantee payment to the merchant, since the aggregated transaction is processed at a later date, it will pre-authorize an amount, for example $15, the first time the customer makes a purchase at that merchant.
Alternatively, merchants can opt for Cardis’ prepaid system. This involves the consumer setting up a prepaid account hosted by Cardis’ sponsoring bank that is topped up via ACH (automated clearing house) transfers. Using the Cardis prepaid account on a smartphone provides the digital equivalent to cash.
With its post-paid solution, merchants will save 30-50 percent per transaction compared to conventional card processing fees, while its prepaid solution saves merchants 80 percent per transaction. With the post-paid solution, it will only aggregate a customer’s purchases at a single specific merchant. But, as the prepaid solution aggregates the customer’s purchases across multiple merchants, this enables to offer a much lower processing fee to the merchant.
Cardis provides an audit trail enabling consumers to track individual transactions that are aggregated using its technology. Consumers don’t lose any of their card protection rights and guarantees by agreeing to let a merchant aggregate their payments through Cardis. They can always charge back any disputed transactions.
Cardis sees opportunities for digital content providers such as online music stores and games providers to use its aggregation technology. It can integrate solution with existing digital wallets.
Raiffeisen
In 2012, Austria’s Raiffeisen Bank launched a pilot of Cardis technology for NFC-based Visa V Pay debit card payments in partnership with Visa Europe. Raiffeisen’s MobileCard mobile payment product uses a secure element stored on an NFC-enabled MicroSD card inserted in a mobile phone. Although Cardis supports secure elements stored on SIM cards as well as on MicroSD cards and on the cloud, Raiffeisen opted for MicroSD cards, as this is an easier solution to implement.
Raiffeisen cardholders participating in the pilot use MobileCard on average three times a week, with an average transaction value of ($5.70). Merchants accepting MobileCard are seeing 40 percent to 70 percent lower merchant processing fees for an average transaction value of ($5.43) to ($13.60).
Spindle
In October 2013, Spindle, a U.S. mobile commerce company, signed an agreement with Multi-max, a manufacturer of vending machines for mid-size and small offices throughout North America, Europe and Asia. Spindle will integrate its MeNetwork mobile commerce technology into Multi-max’s line of K-Cup vending machines for rollout across the U.S.
The MeNetwork solution will incorporate all card-based payment acceptance services, as well as mobile marketing services. Spindle’s partner Cardis will provide low-value payment processing services for purchases at K-Cup vending machines.
Posted in Credit card Processing, Credit Card Security, Digital Wallet Privacy, e-commerce & m-commerce, Electronic Payments, Gift & Loyalty Card Processing, Internet Payment Gateway, Mobile Payments, Mobile Point of Sale, Near Field Communication, Payment Card Industry PCI Security, Smartphone, smartSD Cards, Visa MasterCard American Express Tagged with: accept, ach, aggregated, aggregation, aggregator, authorization, automated clearing house, average transaction, batched, card payments, card processing infrastructure, card processing systems, card-based payment acceptance, cardholders, clearing, contactless, contactless payments, cost-per-transaction, credit card transaction, debit card payments, Digital wallets, high processing charges, low-value payments, merchant aggregate, Merchant's, microSD, mobile app, mobile commerce, mobile payment, Mobile Payments, mobile site, mobile wallet transactions, nfc-based, payment service providers, pre-authorize, prepaid, processed, Processing, processing cost, processing fees, processor, settlement, smartphone, transactions, transfers
November 18th, 2013 by Elma Jane
Big players are entering the merchant cash advance business and the industry’s smaller players are maturing. Meanwhile, the market is growing with the help of automated clearinghouse transactions.
The industry has caught the attention of high rollers who are transforming merchant cash advance into a mainstream option for funding small to midsize businesses.
In the past two years, venture capitalists and hedge funds have invested tens of millions of dollars in long-standing merchant cash advance firms and startups alike.
Meanwhile, big players such as PayPal and the card brands have launched their own programs to provide working capital to merchants.
The business has changed so much in the five years, it’s almost not the same business anymore, says a hybrid ISO and merchant cash advance company based in New York.
CEO of Capital Stack LLC, a merchant cash advance company in New York, has been monitoring the industry’s growth on his DailyFunder blog. He estimates that a year ago, there were about 50 merchant cash advance funders and about $1.5 billion in funding. This year, that number is north of 120, and the funding volume has doubled to $3 billion.
Counting mainstream funders such as Amazon and PayPal, which offer products that follow the cash advance model, the numbers are closer to $5 billion.
Until now, ISOs were using cash advances as an acquiring tool for credit card accounts. An estimate that of the 20 million to 25 million businesses in the U.S., about 5 million accept credit cards. When ACH opened up the remainder of those businesses for loans, the funding volume went off the charts. Now it’s going to grow 50-fold in a 10-year period, just because there are so many more businesses that are approvable.
The popularity of cash advance is good news for ISOs, who might have an easier time pitching the product to merchants because they already know about it and know to ask for it.
A number of factors have coincided to make merchant cash advances more attractive.
Previously, cash advances were associated with luring merchants into a high-rate source of cash. Funders could charge any rates they wanted because the industry was so unregulated. As the industry has matured, the more disciplined companies have survived, while the others have fallen by the wayside, and with the recession causing fewer banks to offer traditional loans, the market is wide open for alternative funders of all shapes and sizes to enter the fray.
The industry has also outgrown the one-size-fits-all pricing that once defined it. Before, all lenders set high prices. Now, companies rely on risk-based pricing, which means better clients get better deals, and ISOs can offer more competitive pricing. That changed the dynamics of the industry.
But the real change in merchant cash advance, members of the industry say, has been the widespread use of automated clearinghouse payment transfers. It used to be that merchant cash advance was available only to companies that accepted credit cards. Now with more businesses accepting payments online via ACH, there is another mechanism for collecting from merchants.
It took some time for people to accept people going into their bank account and debiting their account. Five or six years ago, no one would have allowed someone to do something like that.
Today, everybody’s fundable, as long as you have a bank account. Gone are the days when ISOs had to walk away from potentially big deals because the merchant didn’t accept credit cards, or didn’t have enough processing volume. ISOs and merchants now have more flexibility to walk into just about any business and offer financing. That’s why it’s mainstream.
Posted in Best Practices for Merchants, Financial Services, Merchant Cash Advance Tagged with: accept credit cards, accounts, ach, acquiring, Amazon, approvable, automated, clearinghouse, credit-card, funders, funding, high rate, high rollers, ISO, merchant cash advance, PayPal, traditional loans, transactions, unregulated, venture capitalist, working capital
October 17th, 2013 by Elma Jane
VeriFone and National Payment Card Association (NPCA) debuted a mobile payment and rewards solution that enables convenience store and petroleum retailers to provide customers with smartphone-based payment options at the pump.
Utilizing VeriFone’s Smart Fuel Controller and NPCA’s mobile payment solution, c-store and gas station operators with VeriFone payment acceptance systems can quickly implement a fixed low-cost mobile payment and rewards program built on existing infrastructure used for merchant branded debit cards.
Consumers are increasingly drawn to rewards-based fuel purchase programs and they expect to be able to use their mobile phone to complete transactions at the pump. NPCA and VeriFone are showing how easy it is for CSPs to offer mobile payment and reward options to customers that increase loyalty and sales.
VeriFone Smart Fuel solutions make it easy for CSPs to offer forecourt pump POS payment without incurring the cost of installing new dispensers. The Smart Fuel Controller combines pump and pay-point support into a single unit, simplifying installation and maintenance, and eliminating the need for third-party interface devices to integrate pay-point management with in-store POS systems.
Merchants can develop their own mobile app, or apply their brand to a mobile app supplied by NPCA, to enable customers to pay for purchases and receive loyalty incentives using their smartphones.
Consumers today would rather utilize the capabilities of their smartphones versus pulling out their wallets. Using this solution, retailers can easily and cost-effectively create mobile loyalty programs that attract and reward high-value customers – without having to replace their existing payment infrastructure.
NPCA’s debit-based payment programs provide retailers with the ability to drive customer loyalty and reduce the cost of payments. Fuel discounts are funded from interchange savings that retailers would otherwise pay to banks. Payment processing is done by NPCA using the automated clearing house (ACH) system to clear debits to cardholder checking accounts and net settle with retailers each day. The company holds five patents related to the processing and methods for ACH-based decoupled debit and mobile payments.
Come November VeriFone and NPCA mobile payments solution will be available for beta testing.
Posted in Electronic Payments, Mobile Payments, Point of Sale, Smartphone, Visa MasterCard American Express Tagged with: acceptance, ach, app, apply, cardholder, consumers, cost, debit cards, devices, infrastructure, interchange, interface, loyalty, merchant, mobile, pay-point, payment, payments, phone, POS, Processing, rewards, sales, smart, Smartphones, solution, transactions, verifone, wallets
October 15th, 2013 by Elma Jane
What is an electronic check?
Electronic Check also known as Echeck – is an electronic version of a Paper Check. Electronic Checks allow merchants to convert paper check payments made by customers to electronic payments that are processed through the (ACH) Automated Clearing House Network. It’s a fast, efficient, and secure way to process check payments.
Because of the many benefits and increased security methods that electronic checks offer, this method of payment is quickly growing in popularity. In 2007, electronic check conversion increased by 30%, with more than 3.1 billion paper checks converted to echecks through in-store transactions. Familiarizing yourself with how electronic checks work, the benefits and security features they offer, and how you can get started with electronic check conversion will save you time and money and help you provide greater protection for your business and your customers.
How it works:
Electronic check conversion is a simple method of processing payments, and the changes to how you do business are minimal. One of this method’s greatest advantages is that you can electronically submit checks instead of having to physically take them to the bank, saving you time and increasing employee efficiency.
When you receive a paper check payment from your customer, you will run the check through an electronic scanner system supplied by your merchant service provider like National Transaction Corporation (NTC). This virtual terminal captures the customer’s banking information and payment amount written on the check. The information is transferred electronically via the Federal Reserve Bank’s ACH Network, which takes the funds from your customer’s account and deposits them to yours.
Once the echeck has been processed and approved, the virtual terminal will instantly print a receipt for the customer to sign and keep. Employees should mark the paper check as “void” and return it to the customer. Your merchant transactions will be available online for viewing with customized detailed reporting, which may vary in features depending on the merchant service provider you choose.
Using electronic check conversion to process your customers’ payments holds many benefits over paper checks:
Benefits:
1. Received Funds Sooner. Businesses that use electronic check conversion have funds deposited almost twice as fast as those using the traditional check processing method, with billing companies often receiving payments within one day.
2. Reduced Fraud and Fewer Errors. Echecks are processed using an automated system, which cuts down the number of people who must handle the check, reducing the potential for error and fraud. Merchant service providers (NTC) also maintain, monitor, and check files against negative account databases that store information about individuals or companies that have past records of fraud to help decrease fraudulent activity.
3. Reduced Processing Costs. In general, the cost to process an echeck is substantially less than that of paper check processing or credit card transactions. Echecks require less manpower to process and eliminate incidental costs such as deposit and transaction fees that accompany paper checks. With Echecks, you can save up to 60% in processing fees.
4. Sales Increase. If your business didn’t accept paper checks in the past, you can expand the payment options available to your customers and increase sales by offering echecks. If you are converting from accepting paper checks to echecks, you can still expand your customer base by being able to accept international and
out-of-state checks without the worry of fraud. Echecks require account validation and customer authentication processes that identify bad checks within seconds.
5. Safe, Simple and Smart. Electronic check conversion is easy to set up and relies on the ACH Network for processing, the same reliable and trusted funds transfer system that handles Direct Deposit and Direct Payment. Plus, echecks are a smart choice for the environment, helping to reduce more than 67.4 million gallons of fuel used and 3.6 million tons of greenhouse gas emissions created by transporting paper checks.
Increase security with electronic checks – Electronic check conversion leverages the latest information protection features such as encryption and message authentication. Because of this, many retail merchants, merchant service providers, and financial institutions consider it to be one of the most secure payment methods in the electronic payment processing industry.
Authentication – Merchants must verify that the person providing the checking account information has the authority to use that checking account. There are a number of authentication services and products available to merchants, including:
Digital Signatures or Digital Certificates are a way of Encrypting information that gives the receiver a more reliable indication that the information was sent by the claimed sender. They are used by programs on the Internet to confirm the identity of a customer to concerned third parties, serving a similar purpose as a handwritten signature. Digital Signatures cannot be easily tampered with or imitated and are easily transportable, thereby making them a reliable method for verifying identity when implemented correctly. Digital Signatures are often used to implement Electronic Signatures, a broader term that refers to any Electronic Data that carries the intent of a signature.
Duplicate Detection and prevention is another way to reduce fraudulent activities. Financial institutions have software and operational controls in place to prevent duplication of the scanned electronic representations of customer checks.
Encryption The ACH Network automatically encrypts messages using 128-bit encryption and a secure sockets layer (SSL).
Public Key Cryptography is an Encryption/Decryption Security Method that uses one key to Encrypt a sent message and another to Decrypt it. With Electronic Check Conversion, the Private Key is a secret mathematical calculation used to create the digital signature on the Echeck, and the Public Key is the corresponding key given to anyone who needs to verify that the sender signed the echeck and that the electronic transfer has not been tampered with. Public Key Cryptography is another way to ensure authenticity of the Electronic Transfer of Funds.
What is the (ACH) Automated Clearing House Network?
The Automated Clearing House (ACH) Network is a funds distribution system that moves funds electronically from one entity to another. This highly reliable and efficient nationwide electronic network is governed by the rules established by the National Automated Clearing House Association (NACHA) and the Federal Reserve (Fed). The ACH payment system also handles debit card transactions; direct deposits of payroll, Social Security, and other government benefits; direct debit payments; and business-to-business payments.
How to get started with Echeck:
Useful advice to help make the implementation of electronic check conversion at your business run smoothly:
Choose a processing company that is well established in the market. While a competitive pricing package may also be of importance, having a processor that is reliable with a good reputation is essential.
Look for a processor that enables you to easily align your current business processes with your new electronic processing system. Ensure that you can easily export customer data and smoothly integrate the electronic payment processing system with your business management software.
Notify your customers that your business will begin using electronic check conversion to process payments. Federal rules require you to post a notification about this change in practice as well as to give your customers a takeaway copy of the notification. You must also provide customers a telephone number to request more information about electronic check conversion.
Posted in Electronic Check Services, Electronic Payments, Financial Services Tagged with: ach, authentication, automated clearing house, bank, check, checks, conversion, deposited, digital, echeck, electronic, electronically, encryption, fees, in-store, market, merchant, merchant service provider, money, online, payments, process, Processing, reporting, scanner, Security, signature, submit, terminal, transactions, virtual
October 10th, 2013 by Elma Jane
Merchant Cash Advance was originally structured as a lump sum payment to a business in exchange for an agreed upon percentage of future credit card and/or debit card sales.
Notion Merchant Cash Advance companies provide funds to businesses in exchange for a percentage of the businesses daily credit card income, directly from the processor that clears and settles the credit card payment. A company’s remittances are drawn from customers’ debit- and credit-card purchases on a daily basis until the obligation has been met. Most providers form partnerships with card-payment processors and take payments directly from a business owner’s card-swipe terminal.These Merchant Cash Advances are not loans – they are a sale of a portion of future credit and/or debit card sales. Therefore merchant cash advance companies claim that they are not bound by state usury laws which limit lenders from charging excessive interest rates. This technicality allows them to operate in a largely unregulated market and charge much higher interest rates than banks. This structure has some advantages over the structure of a conventional loan. Most importantly, payments to the merchant cash advance company fluctuate directly with the merchant’s sales volumes, giving the merchant greater flexibility with which to manage their cash flow, particularly during a slow season. Advances are processed quicker than a typical loan, giving borrowers quicker access to capital. Also, because MCA providers typically give more weight to the underlying performance of a business than the owner’s personal credit scores, Merchant Cash Advances offer an alternative to businesses who may not qualify for a conventional loan.
Usage Merchant cash advances are most often used by retail businesses that do not qualify for regular bank loans, and are generally more expensive than bank loans. Competition and innovation led to downward pressure on rates and terms are now more closely correlated with an applicant’s FICO score.
Generally there are three different types of repayment methods for the business.
1. ACH (Automated Clearing House) Withholding: When structured as a sale, the finance company receives the credit card processing information and deducts its portion directly from the business’s checking account via ACH. When structured as a loan, the finance company debits a fixed amount daily regardless of business sales activity.
2. Lock Box or Trust Bank Account Withholding: All of the business’s credit card sales are deposited into bank account controlled by the finance company and then the agreed upon portion is forwarded onto the business via ACH (Automated Clearing House), EFT ( Electronic Funds Transfer) or wire. This is the least preferred method since it results in a one-day delay in the business receiving the proceeds of their credit card sales.
3. Split Withholding: When the credit card processing company automatically splits the credit card sales between the business and the finance company per the agreed portion (generally 10% to 22%). This is generally the most common and preferred method of collecting funds for both the clients and finance companies since it is seamless.
Opting for a merchant cash advance is a decision made by small business owners every day of the week across this country. If you’re having a hard time establishing a business line of credit or getting approved for a business loan, a merchant cash advance may very well be the best option available to you to help you finance your business.
Here are reasons why a business cash advance makes sense.
A. Can take out more advances as advance is repaid
Most business loans will not be extended as you pay off your balance, but with a merchant cash advance, you can get more money as you pay off your advance.
B. Even with less-than-perfect credit, you can be approved
No worries about being approved if you have less-than-perfect credit, a high credit score is not a major factor in whether you are can receive business funding from a cash advance.
C. Flexible repayment terms – repayment is based on sales volume, not a flat rate
Some businesses can run into financial hardships with traditional business loans that require flat-rate monthly payments, but with merchant cash advances your monthly payments are dependent on your sales volume. This means that if you have a slow month, you pay back less.
D. Frees up time because of the simple application/approval process
The application and waiting process for a business loan or even a business line of credit can be outstanding –sometimes you have to wait 30 days just to receive notice of approval from your application, add the wait time to the back and forth calls, document signing, etc – and it can be an arduous process. However, by choosing a merchant cash advance, you can quickly qualify online or by phone.
E. Gives you more money in your pocket to improve cash flow
Cash advances can give you the opportunity to receive more money than you would be able to borrow from a bank.
F. Gives you money right away
With a merchant cash advance you literally can have your cash in as little as 72 hours from your applications approval – and most businesses get their funding in less than a week. Now that’s a simple process
G. New business friendly
Many small business loans require that you have a well-established business (2 years or more) to even consider you for business funding. With a cash advance, you can receive funding even if your company is newly in business.
H. No personal liability for repayment of the cash advance
Much unlike with business lines of credit and small business loans, you are not personally responsible for repayment of the advancement.
I. Non-restrictive usage on what you use the funding for
Too many times business owners are restricted by what they can do with their business loans. But, because a cash advance is designed to help you improve your cash flow, you can use your new funds wherever your business needs them.
J. Qualification is easier than with traditional business loans
Banks have a lot of stipulations for businesses that they loan money to or extend credit lines – cash advances have minimal qualifications and high approval rates.
Posted in Best Practices for Merchants, Merchant Cash Advance, Merchant Services Account Tagged with: ach, automated clearing house, bank, business, businesses, capital, cash advance, credit-card, eff, electronic, excessive, flat-rate, funds, loan, loans, merchant, money, online, pay, payments, Processing, purchases, Rates, signing, transfer







