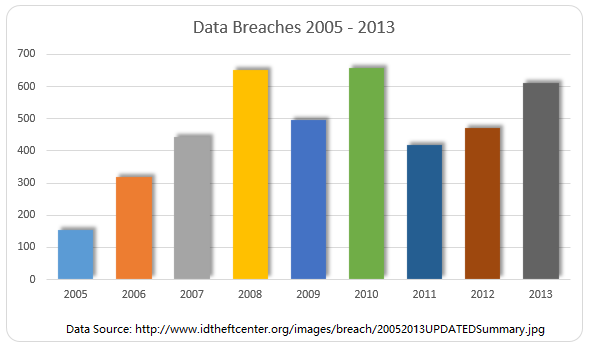
December 28th, 2015 by Elma Jane
Major data breaches were acknowledged by another hotel chain and another brand popular with kids.
Hyatt discovered the intrusion on Nov. 30, which targeted Hyatt-managed properties (not those owned by franchisees), but did not disclose exactly how many properties were affected or how many records may have been exposed. The malware used in the attack targeted payment-card information including cardholder names, PANs, expiration date and CVV/CVC information.
Separately, a security researcher discovered a leaked database from Sanrio, the Japanese company that designs, licenses and produces the popular hello Kitty character. The database reportedly contains account data for 3.3 million users of Sanriotown.com and other Sanrio-owned Websites including hellokitty.com. The company has not yet acknowledged the extent of the breach publicly but said it is investigating.
If so, it is the second network intrusion made public putting the personal information of young people at risk after the Vtech Toy Company Data Breached. Almost 5 million parents and more than 200,000 kids was exposed. The hacked data includes names, email addresses, passwords, and home addresses of 4,833,678 parents who have bought products sold by VTech.
Posted in Best Practices for Merchants Tagged with: card, card information, data, data breaches, payment
September 23rd, 2014 by Elma Jane
Home Depot, US retail chain says that 56 million payment cards are at risk following a malware-laden cyber-attack on eftpos tills across its stores in the US and Canada.
The investigation into a possible breach began on September 2nd,Tuesday morning, immediately after Home Depot received reports from its banking partners and law enforcement that criminals may have breached its systems.
According to Home Depot’s security partners, the malware had not been seen previously in other attacks.
Criminals used unique, custom-built malware to evade detection. The cyber-attack is estimated to have put payment card information at risk for approximately 56 million unique payment cards, after lurking in the company’s eftpos tills for four months between April and September.
While the breach has been seen as a further proof-point in the US push to adopt Chip and PIN at the point-of-sale, the fact that the outbreak also hit the home improvement chain’s Canadian stores, where the EMV standard has been implemented, leaves pause for thought. Nonetheless, the retailer has committed to installing 85,000 PIN pads at its US outlets, well ahead of the national 2015 deadline.
Home Depot has set aside $65 million to cover the cost to investigate the data breach, provide credit monitoring services to its customers, increase call center staffing, and pay legal and professional services. Approximately $27 million of the projected outlay will be covered by the company’s insurance.
Posted in Best Practices for Merchants, EMV EuroPay MasterCard Visa, Point of Sale Tagged with: banking partners, Breach, call center, card information, cards, Chip and PIN, credit monitoring, credit monitoring services, customers, cyber-attack, data breach, EMV, EMV standard, Malware, payment, payment card information, payment cards, PIN pads, point of sale, risk
August 21st, 2014 by Elma Jane
Package delivery giant UPS has become the latest company to admit that customer payment card details may be at risk after it discovered malware at 51 of its US stores. In a statement, UPS says that customers who used credit and debit cards at 51 of its 4470 franchised sites between 20 January and 11 August are at risk. Names, postal and email addresses and payment card information may all be compromised, but UPS says that it has no evidence of any fraud, and that the malware has now been eliminated. Earlier this month the US government took the step of putting out an alert warning retailers about a new family of malware, dubbed Backoff, targeting point-of-sale systems. The UPS Store, received a bulletin from the government among many other US retailers that made them aware of the problem. As soon as they became aware of the potential malware intrusion, they deployed extensive resources to quickly address and eliminate the issue. Customers can be assured that they have identified and fully contained the incident. US merchants have found themselves under siege from hackers in recent months, with the most notable case seeing thieves use a vendor’s credentials to infect POS devices with malware and steal the details of around 40 million Target customer cards.
Posted in Best Practices for Merchants, Credit Card Security Tagged with: card, card details, card information, credit, customer, customer cards, debit cards, devices, fraud, Malware, Merchant's, payment, point of sale, POS, retailers
June 24th, 2014 by Elma Jane
Compliance with a single set of regulations is often taxing enough, without other regulations causing a conflict, but this is exactly the situation that the insurance industry finds itself in with its contact centres.
PCI-DSS compliance insists that sensitive information in particular credit card numbers, must be protected and cannot be stored. However, the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA), the UK regulator for the financial services industry, demands that insurers keep sufficient detail of their transactions.
In insurance contact centres, FCA recommendations are met by recording calls. So in order to comply with PCI-DSS regulations, some contact centres simply pause recordings while the card information is read out, and resume recording once the payment process is complete. There’s a very big problem with this method, it undermines the very reason calls are recorded. The call recording is there to provide an unequivocal record of the circumstances under which the policy is granted. A gap in this record creates doubt. What was said during this time? If a customer is claiming a policy is mis-sold or they were misinformed in some way, a complete record to refute this claim no longer exists. Because of situations such as this, the insurance industry has an inherent dependence on contact centres and person-to-person interaction when selling policies, though in the process has to somehow comply with both regulations. But how? One way is to get the sensitive card information directly and securely to the bank’s payment gateway without storing it. Online, this is done quite easily, insurers can embed a secure payment page into a website and the customer can enter information securely that way. By phone a similar method can be used. A caller can input information directly on their telephone keypad and the tones are only transmitted to the credit card payment gateway not the contact centre. This solves the paradox of the conflicting regulations.
Insurance contact centres need to walk a very fine line, ensuring that they comply with all of the relevant regulations from multiple regulators – even those that, at first glance, contradict each other.
Posted in Best Practices for Merchants, Credit Card Security, Payment Card Industry PCI Security Tagged with: (FCA), card information, compliance, contact centres, credit card payment, credit-card, customer, Financial Conduct Authority, financial services industry, insurance industry, payment gateway, payment process, PCI-DSS, phone, regulations, secure payment, taxing, telephone keypad, transactions, website



