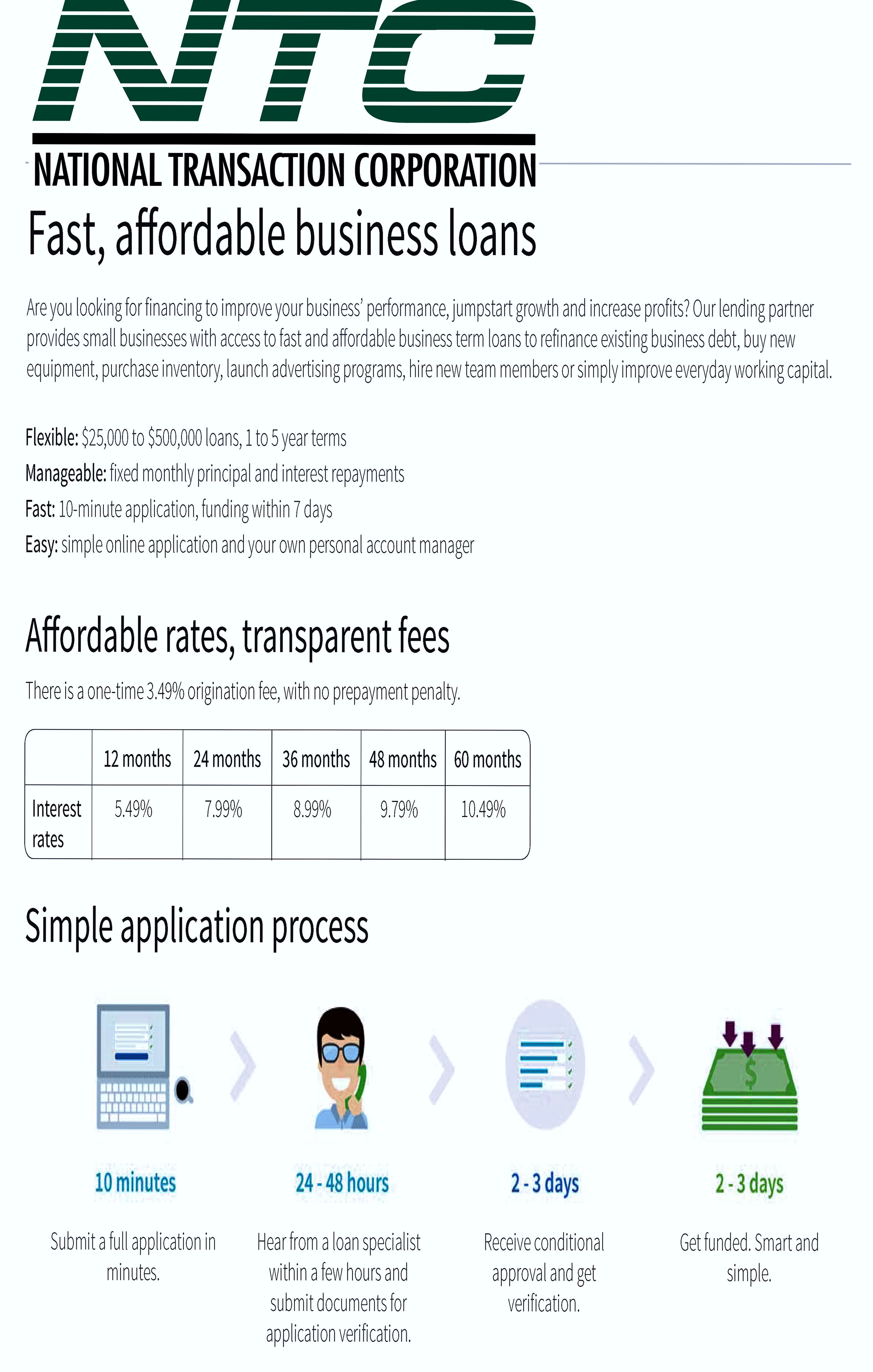
July 19th, 2016 by Elma Jane
Here are some of the Common Business Loan Fees:
Application Fee – is a fee charged to cover the costs of processing and assessing your loan application.
Bank Wire Fee – When borrowing a loan, lenders commonly wire the money to your bank account via ACH, because the banks need to talk to each other and ensure the money is going to the right place and that no fraud is going on.
Check Processing Fee – ACH transfers are commonly used to collect periodic repayments from the debtor’s bank account. Some lenders offer the option of paying by check, but you’ll have to pay a fee for the extra cost involved.
Closing Cost – not to be confused with closing fees, encapsulate all the fees charged for processing a loan, including origination/closing fees, processing fees, referral fees, and/or packaging fees.
Draw Fee – similar to an origination fee, but is applicable instead for lines of credit.
Guarantee Fee – is charged on all SBA loans above $150K. Guarantee fee is charged to protect against credit-related losses in the mortgage portfolio.
Late Payment Fee – Missing a payment deadline can result in a late fee. A late payment may have an affect on your personal or business credit score.
Origination Fee – an up-front fee charged for processing a new loan application. Prepayment
Penalty – Is a borrower, a bank or mortgage lender agreement that regulates what the borrower is allowed to pay off and when.
Servicing and Maintenance Cost – fees charged to cover the costs associated with collecting payments, maintaining records, following up on delinquencies and any other costs associated with maintaining a term loan or line of credit.
Business loans are available in different types, from merchant cash advances to lines of credit. The most effective way to get the best deal on a business loan is to be educated and know that Fees are Negotiable.
Posted in Best Practices for Merchants, Financial Services Tagged with: ach, bank account, check, credit, fee, fraud, loan, payment
May 26th, 2015 by Elma Jane
MasterCard is aiming to change the way people transfer money between debit cards, with its new program called MasterCard Send. This first-of-its-kind, global personal payments platform allows consumers to send and receive funds within seconds, rather than waiting for the standard 1-3 business day transfer time.
Unlike most person-to-person (P2P) processors like PayPal, MasterCard Send is not designed specifically for consumers. Instead, it aims to help businesses send disbursements and cash back to customers in something very close to real-time.
Customers can receive direct deposits into their debit card accounts for shipping rebates. There is no waiting for a check in the mail or a long transfer process.
Consumers can still use MasterCard Send to send and receive money from friends and family members. The recipient does not need a debit card to access the funds. Send will also work with programs like Western Union.
According to MasterCard, cash and checks still contribute $1 trillion in global spending every year. MasterCard Send is attempting to be a safer, faster and cheaper alternative to these transactions. The program is now live in the United States.
MasterCard Send is addressing a real need that exists in today’s digital world to enable consumers, businesses, governments and more to have a safe, simple and secure way to transfer and receive funds quickly.
Posted in Financial Services Tagged with: card accounts, cash back, check, consumers, debit cards, direct deposits, funds, MasterCard, p2p, payments, processors, transactions
September 4th, 2014 by Elma Jane
EMV, which stands for Europay, MasterCard and Visa, and is slated to be mandated across the United States starting in October 2015 and automated fuel dispensers have until October 2017 to comply. Unlike magnetic swipe cards, EMV chip cards encrypt data and authenticate communication between the card and card reader. Additionally, chip card user is prompted for a PIN for authentication.
Why are those dates important? Companies lose $5.33 billion to fraud today, with card issuers and merchants incurring 63 and 37 percent of these losses, respectively. Under the EMV mandate, merchants who do not process chip cards will bear the burden of the issuer loss. By accepting chip card transactions, merchants and issuers should see a reduction in fraud.
Overcoming Barriers to EMV Adoption
Given the significant barriers to EMV adoption, it may be tempting for merchants to meet minimum requirements for accepting EMV payments. However, medium to large retailers should also consider the bigger picture of customer security and peace of mind.
Some key critical success factors for a payment initiative of this size include:
Business Continuity Architecture: As with all payment systems, it is imperative to have the EMV system running at all times. The solution should preferably have Active-Active architecture across multiple data centers and have a low Recovery Point Objective (the point in time to which the systems and data must be recovered after an outage).
Cost Benefit Analysis: Take a top down approach and decide accordingly on the scope of the analysis. This will ensure that decisions on scope are made on basis of quantitative data and not just qualitative arguments.
Phased Approach: To overcome time or cost overage in a project of this scope and complexity, retailers should try using an iterative approach for development. The rollout can be divided into multiple releases of six to seven months, which will provide the opportunity to review, capture lessons learnt, and improve subsequent releases.
Proactive Monitoring Alerts: Considering the criticality of business function carried out by EMV, tokenization and payment gateway, a vigorous supervising environment must be defined to perform proactive and reactive monitoring. It should take into consideration the monitoring targets, tools, scope and methods. This will provide advance visibility to the failure points and better ensuring maximum system availability.
Resilience Testing: Typically in a software project, the testing is limited to the unit, integration, performance and user acceptance. However, due to the critical nature of the applications and systems involved, robust resiliency testing is vital. This will ensure that there are no single points of failure and the system remains available when running in error conditions.
Stakeholder Identification: This is a key step to ensure that you have varied perspectives from all departments and their support. It will keep your organization from being blindsided and reduce the risk of disagreements in later stages of the program. Key stakeholders should include Store Operations, Card Accounting, Loss Prevention, Contact Center and IT & Data Security.
Organizations should adopt a five step approach to implement a secure, robust and industry-leading payment solution:
Encryption – Point to point encryption will ensure card data is secure and encrypted from the point of capture to the processor. Usually, merchants use data encryption that is not point to point, rendering their organization vulnerable to data breaches. Software encryption is the most common form of encryption, as it is easily installed and quires little or no hardware upgrades; however, it is less secure, may expose encryption keys, and is prone to memory scanning attacks. Hardware encryption is considered more secure but requires more costly terminal upgrades. Hardware encryption is designed to self-destruct the keys if tampered, but is not well-defined as very limited headway has been made in this space.
Tokenization – Build a Card Data Environment (CDE) that will host a centralized card data storage solution. Only limited applications with firewall access and capability to mutually authenticate via certificates can access CDE and receive card data. The rest of the applications will have tokens which are random numbers. This architecture will ease the merchant’s burden with existing and emerging PCI Data Security Standards.
Payment Gateway – Perform a risk assessment on the current payment gateway and identify gaps in functionality, manageability, compliance, scalability, speed to market and best practices. Determine the alternatives to mitigate the risks. Some of the important aspects of a leading payment gateway solution are support for all forms of credit, debit, gift cards and check transactions. Its ability to work with any acquirer, in-built encryption abilities, support for settlement and reconciliation must also be kept into consideration.
Settlement, Funding and Reconciliation – A workflow-based system to handle chargebacks and the automation of chargeback processing will greatly reduce labor-intensive work and enhance the quality of data used for settlement and reconciliation. Upgrades to the existing receipt retrieval system may be needed.
Card fraud is on the rise in the U.S., and merchants are the primary target for stealing information. With the EMV deadline just over a year away, the responsible retailer must take steps to prepare now. Although EMV implementation might seem overwhelming to merchants, they should start their journey to secure payments rather than wait for a looming deadline. Solutions such as data encryption and tokenization should be used in combination with EMV to implement a robust payment solution to better protect merchants against fraud. By proactively adopting EMV payment solutions, merchants can stay ahead of the regulatory curve and better protect their customers from fraud.
Posted in Best Practices for Merchants, Credit Card Security, EMV EuroPay MasterCard Visa, Payment Card Industry PCI Security, Visa MasterCard American Express Tagged with: authentication, automation, card, card data, Card Data Environment, card fraud, card issuers, card transactions, CDE, chargeback, chargeback processing, check, check transactions, chip, chip cards, credit, customer, customer security, data, data breaches, data encryption, data security, debit, EMV, emv chip cards, EuroPay, fraud, gateway, Gift Cards, host, integration, magnetic swipe cards, MasterCard, Merchant's, payment, payment gateway, payment solution, payment systems, PCI, PCI Data Security Standards, PIN, processor, retailers, Security, software, swipe, terminal, tokenization, tools, visa
October 15th, 2013 by Elma Jane
What is an electronic check?
Electronic Check also known as Echeck – is an electronic version of a Paper Check. Electronic Checks allow merchants to convert paper check payments made by customers to electronic payments that are processed through the (ACH) Automated Clearing House Network. It’s a fast, efficient, and secure way to process check payments.
Because of the many benefits and increased security methods that electronic checks offer, this method of payment is quickly growing in popularity. In 2007, electronic check conversion increased by 30%, with more than 3.1 billion paper checks converted to echecks through in-store transactions. Familiarizing yourself with how electronic checks work, the benefits and security features they offer, and how you can get started with electronic check conversion will save you time and money and help you provide greater protection for your business and your customers.
How it works:
Electronic check conversion is a simple method of processing payments, and the changes to how you do business are minimal. One of this method’s greatest advantages is that you can electronically submit checks instead of having to physically take them to the bank, saving you time and increasing employee efficiency.
When you receive a paper check payment from your customer, you will run the check through an electronic scanner system supplied by your merchant service provider like National Transaction Corporation (NTC). This virtual terminal captures the customer’s banking information and payment amount written on the check. The information is transferred electronically via the Federal Reserve Bank’s ACH Network, which takes the funds from your customer’s account and deposits them to yours.
Once the echeck has been processed and approved, the virtual terminal will instantly print a receipt for the customer to sign and keep. Employees should mark the paper check as “void” and return it to the customer. Your merchant transactions will be available online for viewing with customized detailed reporting, which may vary in features depending on the merchant service provider you choose.
Using electronic check conversion to process your customers’ payments holds many benefits over paper checks:
Benefits:
1. Received Funds Sooner. Businesses that use electronic check conversion have funds deposited almost twice as fast as those using the traditional check processing method, with billing companies often receiving payments within one day.
2. Reduced Fraud and Fewer Errors. Echecks are processed using an automated system, which cuts down the number of people who must handle the check, reducing the potential for error and fraud. Merchant service providers (NTC) also maintain, monitor, and check files against negative account databases that store information about individuals or companies that have past records of fraud to help decrease fraudulent activity.
3. Reduced Processing Costs. In general, the cost to process an echeck is substantially less than that of paper check processing or credit card transactions. Echecks require less manpower to process and eliminate incidental costs such as deposit and transaction fees that accompany paper checks. With Echecks, you can save up to 60% in processing fees.
4. Sales Increase. If your business didn’t accept paper checks in the past, you can expand the payment options available to your customers and increase sales by offering echecks. If you are converting from accepting paper checks to echecks, you can still expand your customer base by being able to accept international and
out-of-state checks without the worry of fraud. Echecks require account validation and customer authentication processes that identify bad checks within seconds.
5. Safe, Simple and Smart. Electronic check conversion is easy to set up and relies on the ACH Network for processing, the same reliable and trusted funds transfer system that handles Direct Deposit and Direct Payment. Plus, echecks are a smart choice for the environment, helping to reduce more than 67.4 million gallons of fuel used and 3.6 million tons of greenhouse gas emissions created by transporting paper checks.
Increase security with electronic checks – Electronic check conversion leverages the latest information protection features such as encryption and message authentication. Because of this, many retail merchants, merchant service providers, and financial institutions consider it to be one of the most secure payment methods in the electronic payment processing industry.
Authentication – Merchants must verify that the person providing the checking account information has the authority to use that checking account. There are a number of authentication services and products available to merchants, including:
Digital Signatures or Digital Certificates are a way of Encrypting information that gives the receiver a more reliable indication that the information was sent by the claimed sender. They are used by programs on the Internet to confirm the identity of a customer to concerned third parties, serving a similar purpose as a handwritten signature. Digital Signatures cannot be easily tampered with or imitated and are easily transportable, thereby making them a reliable method for verifying identity when implemented correctly. Digital Signatures are often used to implement Electronic Signatures, a broader term that refers to any Electronic Data that carries the intent of a signature.
Duplicate Detection and prevention is another way to reduce fraudulent activities. Financial institutions have software and operational controls in place to prevent duplication of the scanned electronic representations of customer checks.
Encryption The ACH Network automatically encrypts messages using 128-bit encryption and a secure sockets layer (SSL).
Public Key Cryptography is an Encryption/Decryption Security Method that uses one key to Encrypt a sent message and another to Decrypt it. With Electronic Check Conversion, the Private Key is a secret mathematical calculation used to create the digital signature on the Echeck, and the Public Key is the corresponding key given to anyone who needs to verify that the sender signed the echeck and that the electronic transfer has not been tampered with. Public Key Cryptography is another way to ensure authenticity of the Electronic Transfer of Funds.
What is the (ACH) Automated Clearing House Network?
The Automated Clearing House (ACH) Network is a funds distribution system that moves funds electronically from one entity to another. This highly reliable and efficient nationwide electronic network is governed by the rules established by the National Automated Clearing House Association (NACHA) and the Federal Reserve (Fed). The ACH payment system also handles debit card transactions; direct deposits of payroll, Social Security, and other government benefits; direct debit payments; and business-to-business payments.
How to get started with Echeck:
Useful advice to help make the implementation of electronic check conversion at your business run smoothly:
Choose a processing company that is well established in the market. While a competitive pricing package may also be of importance, having a processor that is reliable with a good reputation is essential.
Look for a processor that enables you to easily align your current business processes with your new electronic processing system. Ensure that you can easily export customer data and smoothly integrate the electronic payment processing system with your business management software.
Notify your customers that your business will begin using electronic check conversion to process payments. Federal rules require you to post a notification about this change in practice as well as to give your customers a takeaway copy of the notification. You must also provide customers a telephone number to request more information about electronic check conversion.
Posted in Electronic Check Services, Electronic Payments, Financial Services Tagged with: ach, authentication, automated clearing house, bank, check, checks, conversion, deposited, digital, echeck, electronic, electronically, encryption, fees, in-store, market, merchant, merchant service provider, money, online, payments, process, Processing, reporting, scanner, Security, signature, submit, terminal, transactions, virtual



