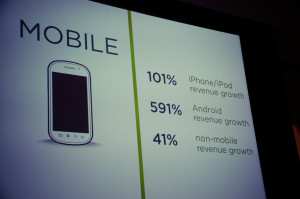
September 10th, 2020 by Admin
There are few moments like now where American consumers are collectively open to the idea of new payment methods – especially contactless ones such as mobile wallets. This is good news for businesses since mobile wallets offer a safer payment alternative to credit cards and drastically reduce customer wait times at checkout.
Mobile wallets (such as Apple Pay and PayPal) use authentication, monitoring and data encryption to secure and transmit personal information, and the level of security associated with them has payment card issuers backing their use. This is certainly helping drive consumer adoption, as does convenience.
In fact, global mobile wallet transaction value is estimated to reach nearly $14 trillion by 20201 – and that is a pre-COVID-19 estimate. New estimates are higher and point to further rapid adoption given the current need for touch-free payment options. According to a recently published Visa Back to Business report,* 70 percent of consumers surveyed in June 2020 have used a new shopping or payment method for the first time this year.
A rapid shift has begun and the numbers tell the storySo what is holding back business adoption of mobile wallets? Until recently, it just wasn’t a priority for many small- and medium-size businesses to enable it or educate their employees on its use. The lack of preferential demand didn’t make it a pressing topic. But that is changing. Consider this:
- According to Forbes,2 by 2026, digital natives will be 59 percent of the consumers in the U.S. market.
- Of this, 45 percent will be specifically Millennials and Gen Z, representing the largest purchasing power.
- As Gen Z move into becoming the largest generation cohort, their purchasing power will be $143 billion.
But it’s not just what lies ahead that SMBs should be focused on now.
According to Visa’s Back to Business report, shoppers are now putting COVID-19 safety measures at the top of their shopping lists and they will reward stores that do the same. In fact, if all other factors were equal (price, selection, location), nearly 63 percent of consumers surveyed would switch to a new store that installed contactless payment options, such as mobile wallets.3
What does this mean for you? Now is the time to connect with customers to make sure they are fully contactless capable and have the technology in place to accept many of the most popular mobile wallets.
1Payments Industry Intelligence, “The rise of digital and mobile wallet: Global usage statistics from 2018,” November 25, 2018.
2Forbes, January 2020
3Visa Back to Business report 2020
Posted in Digital Wallet Privacy, e-commerce & m-commerce, Electronic Payments, Internet Payment Gateway, Mobile Payments, Uncategorized Tagged with: business, digital payment, digital payments, Digital Wallet, Digital wallets, mobile, mobile commerce, Mobile Devices, mobile payment, Mobile Payments, mobile wallet, mobile wallets, payment, payments

September 24th, 2015 by Elma Jane
If you accept credit cards and don’t know what EMV is here is what you need to know.
EMV stands for Europay, MasterCard and Visa. A credit card that had a chip embedded in it is an EMV. EMV Cards have been standard in Europe for more than 10 years because they’re more secure than magnetic stripe cards. Magnetic stripe cards doesn’t change, it has static data, which makes them easy to clone. The chip embedded card makes it more difficult and costly to counterfeit because the data that is transmitted changes each time the card is read. This means less fraud.
Questions to ask to help you decide about terminal upgrade.
- Calculate your risk – Consider the cost of replacing your point-of-sale (POS) terminal vs. potential risk. Whether you replace it now or at a later time, eventually all businesses will have to replace their POS terminals.
- Educate your staff – Educated employees translate to better-educated customers. Merchants can help customers better understand this change and what it means for them.
- Upgrade your POS system – Consider using an EMV compliant credit-card reader on a wireless device for an ultra-secure mobile solution. This is also a chance to upgrade other options, such as near field communication NFC technology, which lets consumers use their mobile devices to make payments at the point of sale.
Posted in Best Practices for Merchants, Credit Card Reader Terminal, Credit Card Security, EMV EuroPay MasterCard Visa, Mobile Point of Sale, Near Field Communication, Point of Sale Tagged with: chip, credit card reader, credit cards, data, EMV, emv cards, EuroPay, magnetic stripe cards, MasterCard, merchants, Mobile Devices, Near Field Communication, nfc, payments, point of sale, POS terminal, visa
October 13th, 2014 by Elma Jane
Non-cash payments volumes are expected to increase by nearly 10% percent to reach 366 billion transactions in 2013, fueled by strong growth in developing markets and mobile payments.
Overall, more than half of global non-cash payment growth comes from developing countries despite them only making up one quarter of the market size at 93 billion transactions. China remains a relatively underdeveloped market for non-cash transactions but its population and growth rate suggest in certain conditions that it could soon outstrip the US and Euro-zone within the next five years.
China is one to watch over the coming years, with the report showing that if growth rates remain at the current high level, it could become the largest market for non-cash transactions within just five years. These soaring growth rates in key markets put pressure on the global payments arena to innovate to meet rapidly increasing consumer demand.
Increased use of tablets and smartphones is creating a convergence of e- and m- payments, posing new challenges for Payments Services Providers (PSPs). In 2015, m-payments are projected to grow at 60.8% while e-payments growth is forecast to decelerate to 15.9% annually over the next year, as more people use mobile devices to make payments.
This trend is adding to the pressure on PSPs to modernize their payments processing infrastructures, ideally based around a single integrated payments platform for corporate and retail payments and a central hub.
The growth of the industry coupled with the fast pace of new regulation requires flexibility from PSPs to adapt, initiatives such as real-time payments, pressure on card interchange fees and improved payments governance as examples of cascading regulation.
Posted in Best Practices for Merchants Tagged with: card, card interchange fees, consumer, e-payments, global payments, m-payments, Mobile Devices, Mobile Payments, Non-cash payments, payments platform, payments processing, Payments Services Providers, psps, real-time payments, retail payments, Smartphones, tablets, transactions
September 15th, 2014 by Elma Jane
Visa has taken advantage of the hoopla surrounding Apple’s application of digital account tokens to replace card numbers for online and mobile purchasing by initiating the roll out of its Token Service to US clients.
Visa Tokens will be made available to issuing financial institutions globally, starting with US banks next month, and followed by a phased roll-out overseas beginning in 2015. The technology has been designed to support payments with mobile devices using all major mobile platforms.
More than 750 staff from across the Visa organisation globally were involved in the effort, working closely with initial launch partners – financial institutions, merchants and processors to ensure the ecosystem was ready. Today, Visa is making these services available and believe it will help transform connected devices and wearables into secure payment vehicles.
Visa Token Service replaces sensitive payment account information found on plastic cards with a digital account number or token. Because tokens do not carry a consumer’s payment account details, such as the 16-digit account number, they can be safely stored by online merchants or on mobile devices to for e-commerce and mobile payments.
The release of the service has been given added urgency by a spate of successful hacks on merchant card data stores, such as the recent plundering of card account data at Home Depot and Target.
MasterCard has its own equivalent Digital Enablement Service, which will be released outside of the US in 2015.
Posted in Best Practices for Merchants, Credit Card Security, e-commerce & m-commerce, Mobile Payments, Visa MasterCard American Express Tagged with: account details, card, card account data, card data, data, digital account, digital account number, e-commerce, financial institutions, MasterCard, merchant card data, Merchant's, mobile, Mobile Devices, Mobile Payments, mobile platforms, online merchants, payments, processors, Token Service, tokens, visa, Visa organisation, Visa Token Service, wearables
September 10th, 2014 by Elma Jane
Merchant go into business to make a sale. They go to great length to advertise their business and then they make a sale and don’t track it… They don’t track the very customer they went into business to attract…That seems crazy…But now more companies are embracing the practice of collecting email addresses at the point of sale (POS) and they’re doing so with increasing regularity. An example, when customers are at the cash register, many brick-and-mortar stores now offer to email them receipts
Confidently collect email addresses at POS:
Your email service provider should be able to implement a text-to-join acquisition program for you that executes quickly and can be built specifically to mitigate the risks around POS data collection.
Instead of relying on sales associates to accurately input email addresses, your customers can use SMS to text their email addresses to your short code.
Customers receive an immediate SMS reply message letting them know to check their email for their receipt.
A mobile-optimized receipt is immediately emailed to the address.
This can be followed by an email inviting customers to join your company’s email program. Offering a purchase discount can increase opt-ins. New joiners can be sent an age verification email, if relevant.
Your welcome email, including discount coupon, is sent and the relationship starts off on the right foot.
Increasing your confidence about POS email address collection, a text-to-join program can increase your acquisition rates. It can engage those customers who prefer to provide their information privately via their mobile devices. It can help protect companies against potential blacklisting because of typos and confirmed opt-ins. It can even reduce overhead costs by saving sales associates valuable time. Understanding these important email address collection issues and adopting the prescribed best practices are critical to ensuring customers have a safe, positive and valuable experience with your company at the point of sale and beyond.
Virtual Merchant can collect data too, and as a provider we can help merchant use that data. We are committed to providing appropriate protection for the information that is collected from customers who visit the website and use the Virtual Merchant payment system. Policy Privacy is updated from time to time.The website is provided to our customers as a business service and use of the site is limited to customers only.
If the merchant never makes a sale before 10 why do they open at 9 ?? This is only one small example on how collecting data first and then analyzing that data can shape businesses and find money you may be throwing away ….
Posted in Best Practices for Merchants, Mobile Point of Sale, Point of Sale Tagged with: brick and mortar, business, cash, cash register, customers, data, discount, discount coupon, email, merchant, mobile, Mobile Devices, payment, payment system, point of sale, policy, POS, provider, purchase, Rates, receipts, sale, service, sms, store's, virtual merchant, website
July 21st, 2014 by Elma Jane
PayPal has begun testing a new loyalty program called PayPal Select that seeks to promote use of the digital-payments network by offering more rewards for its most active members. The program launched by invitation only based on users’ history on PayPal and follows by about 18 months the cancellation PayPal’s previous loyalty program, PayPal Advantage. As PayPal looks to continue to build its volume of use on mobile devices off of eBay, driving repeat use and loyalty will be key. The challenges for the offer part will be the same as any other deal/offer program – namely the quality of the offers and inbox-offer fatigue. Like any big-screen concept that gets downscaled onto mobile, there is the challenge of how to hook people in the first couple of screens. CreditCall is not involved with PayPal Select. The payment platform is a division of San Jose, CA-based online auction giant eBay. It offers both a mobile app and an m-dot site for mobile payments.
Posted in Mobile Payments, Smartphone Tagged with: CreditCall, digital-payments network, ebay, loyalty program, m-dot site, mobile, mobile app, Mobile Devices, Mobile Payments, PayPal, PayPal Advantage, PayPal Select, rewards
July 15th, 2014 by Elma Jane
Businesses only stand to benefit by making themselves accessible via mobile devices. With a mobile website or mobile app, businesses can boost sales, retain loyal customers and expand their reach. The question is, which type of mobile presence is best for your business Or should you have both? Both mobile websites and mobile apps let customers find and access your business from devices they use the most, but a mobile website and mobile app are not the same thing. To help you decide, check out the differences between the two and how they can benefit your business.
Mobile App – is a smartphone or tablet application. Unlike a mobile website, a mobile app must be downloaded and installed, typically from an app marketplace, such as the Apple App Store or Android’s Google Play store.
Mobile Website – is designed specifically for the smaller screens and touch-screen capabilities of smartphones and tablets. It can be accessed using any mobile devices Web browser, like Safari on iOS and Chrome on Android. Users simply type in the URL or click on a link to your website, and the website automatically detects the mobile device and redirects the viewer to the mobile version of your website.
Mobile website’s benefits
The primary benefit of a mobile website is that it makes regular websites more accessible for mobile users. It can have all the same elements as the regular version of the website, such as its look and feel, pages, images and other content, but it features a mobile-friendly layout that offers improved readability and functionality when viewed on a smartphone or tablet. By having a mobile website, customers can access your website anytime, anywhere using any device, without compromising the user experience.
Mobile app’s benefits
Although a mobile app functions a lot like a mobile website, a mobile app gives businesses the advantage of having their own corner on a customer’s device, because users have to download and install the app, businesses have more control over their presence on a device than they would with a mobile website. For instance, a mobile app can be closed or inactive, but still work in the background to send geo-targeted push notifications and gather data about customer’s preferences and behaviors. Moreover, mobile apps make it easy to deploy loyalty programs and use mobile payments using a single platform. It’s also much easier to access a mobile app than a mobile website all it takes is one tap, versus having to open a Web browser then type in a URL.
Mobile website and Mobile app features
Although mobile websites and mobile apps aren’t the same thing, they generally offer the same features that can help grow your business by making it easier for customers to find and reach you.
Features include the following:
Click-to-map: Users can use their devices’ GPS to locate your business and instantly get directions, without having to manually input your address.
Mobile commerce: Take your online store mobile with e-commerce-capable mobile websites and apps, such as with Buy Now buttons and mobile carts.
One-click calling: Users can call your business simply by tapping on your phone number from your website or app.
Social sharing: This feature integrates social media apps and websites to enable users to easily share content with friends and followers.
Mobile marketing: This lets users sign up for marketing lists and loyalty programs while enabling businesses to easily launch location-based text-message marketing and email marketing campaigns.
How to build a mobile app
Just like the options available for building a mobile website, businesses can either hire an app developer to build a mobile app or take the budget-friendly DIY mobile app maker route.
How to build a mobile website
To build a mobile website, one option is to hire a mobile Web developer to create one from scratch or convert an existing website into a mobile-friendly one. A more affordable option is to build one yourself with a free DIY mobile website builder, which uses a drag-and-drop platform that doesn’t require programming or Web design skills.
Posted in Uncategorized Tagged with: Android's Google Play, Apple App, Chrome, customers, data, devices, e-commerce, email marketing, GPS, iOS, mobile, mobile app, mobile carts, Mobile Devices, mobile website, platform, programs, Safari, smartphone, tablet, URL, Web browser
June 10th, 2014 by Elma Jane
Local businesses with brick-and-mortar stores have not been early adopters of ecommerce. But, with the proliferation of mobile devices and with changes in how consumers research and buy products, most local businesses now have websites, many of them mobile optimized. Smart brick-and-mortar retailers invest in local search engine optimization to ensure that their stores are found when a local shopper searches on products that they sell. More aggressive retailers also invest in pay-per-click advertising on Google to ensure that their store names, phone numbers, and addresses are visible to a local shopper that is researching on a smartphone. Google is by far the primary search engine used by mobile shoppers. Google favors mobile friendly online stores and rewards mobile sites with high search rankings. The next logical step for local retailers is investing in on online store.
There are several reasons:
1. Having an online store will help local retailers optimize Google rankings for specific products and brands.
2. Being able to show that an item is in stock may eliminate competitive shopping.
3. Eventually local retailers could sell products to consumers outside the retailers’ immediate area, and thus expand their business.
Many local businesses are hesitant to open an online store. Here is why:
1. Local businesses are typically unfamiliar with running an ecommerce business.
2. Have little ability to ship or fulfill online orders.
3. Cannot accommodate sales tax collection outside their local area.
4. Avoid the investment required.
To be sure, adding an online store is not for every local business. But, if a local retailer offers a unique set of products, she may want to evaluate the concept.
Posted in Best Practices for Merchants, e-commerce & m-commerce Tagged with: brands, brick and mortar, brick-and-mortar stores, consumers, ecommerce, google, Mobile Devices, mobile optimized, mobile sites, online orders, online stores, pay-per-click, products, sales tax, search engine, search engine optimization, smartphone, websites
June 5th, 2014 by Elma Jane
The days of salespeople peddling point of sale terminals by simply pulling hardware out of a box are numbered. That model is being replaced by integrated payments from software developers who add payment capabilities to applications that run at the point of sale, in the back office or on mobile devices.
Integrated payments are becoming common in the restaurant industry, where systems are developed to combine payment acceptance with the ability to manage orders, tables and food delivery. As integrated payments become more common, companies working in the payments industry will seek ways to offer marketing analytics. You tie that type of data to the payment mechanism and you can learn more about your business and your customers.
There is a place in the ecosystem for traditional payment acceptance, but today, when a retailer shops for a point of sale terminal or other business solutions, they expect payments to be part of the integrated bundle. Many of these systems are now delivered in a software-as-a-service model or through tablets, making them cost-effective for businesses of any size.
Integrated commerce includes mobile acceptance, offers, coupons and loyalty. It enables a merchant to buy a point of sale system for the physical store, website and mobile environment at the same time. Then the merchant can send out offers and begin running a loyalty program, while accepting NFC transactions all at once. Merchants can also review transactions from all channels directly from their offices to monitor against data breaches. With those integrated services becoming more readily available for merchants, it is not surprising that the topic comes up when executives discuss their company’s goals.
Relationships with merchants through integrated payments tend to be sticky because it is an embedded solution. You tend to get better pricing because it’s not necessarily an acquiring decision but a POS software/hardware decision and acquiring is part of that package. Payments as a service will be an important global product, selling a terminal now means selling data security, warranty and service, and numerous merchant tools.
Posted in Best Practices for Merchants, Credit Card Reader Terminal, Point of Sale Tagged with: breaches, coupons and loyalty, data, data breaches, data security, global product, integrated bundle, Integrated commerce, integrated payments, integrated services, loyalty program, marketing analytics, merchant, merchant tools, mobile, Mobile Devices, NFC transactions, payment, payment mechanism, payments industry, point of sale, POS software/hardware, Security, tablets, terminal, terminals, traditional payment, warranty and service, website and mobile environment
May 21st, 2014 by Elma Jane
Mobile credit card processing is way cheaper than traditional point-of-sale (POS) systems. Accepting credit cards using mobile devices is stressful, not to mention a hassle to set up and customers would never dare compromise security by saving or swiping their credit cards on a mobile device. Some of the many myths surrounding mobile payments, which allow merchants to process credit card payments using smartphones and tablets. Merchants process payments using a physical credit card reader attached to a mobile device or by scanning previously stored credit card information from a mobile app, as is the case with mobile wallets. Benefits include convenience, a streamlined POS system and access to a breadth of business opportunities based on collected consumer data. Nevertheless, mobile payments as a whole remains a hotly debated topic among retailers, customers and industry experts alike.
Although mobile payment adoption has been slow, consumers are steadily shifting their preferences as an increasing number of merchants implement mobile payment technologies (made easier and more accessible by major mobile payment players such as Square and PayPal). To stay competitive, it’s more important than ever for small businesses to stay current and understand where mobile payment technology is heading.
If you’re considering adopting mobile payments or are simply curious about the technology, here are mobile payment myths that you may have heard, but are completely untrue.
All rates are conveniently the same. Thanks to the marketing of big players like Square and PayPal – which are not actually credit card processors, but aggregators rates can vary widely and significantly. For instance, consider that the average debit rate is 1.35 percent. Square’s is 2.75 percent and PayPal Here’s is 2.7 percent, so customers will have to pay an additional 1.41 percent and 1.35 percent, respectively, using these two services. Some cards also get charged well over 4 percent, such as foreign rewards cards. These companies profit & mobile customers lose. Always read the fine print.
Credit card information is stored on my mobile device after a transaction. Good mobile developers do not store any critical information on the device. That information should only be transferred through an encrypted, secure handshake between the application and the processor. No information should be stored or left hanging around following the transaction.
I already have a POS system – the hassle isn’t worth it. Mobile payments offer more flexibility to reach the customer than ever before. No longer are sales people tied to a cash register and counters to finish the sale. That flexibility can mean the difference between revenue and a lost sale. Mobile payments also have the latest technology to track sales, log revenue, fight chargebacks, and analyze performance quickly and easily.
If we build it, they will come. Many wallet providers believe that if you simply build a new mobile payment method into the phones, consumers will adopt it as their new wallet. This includes proponents of NFC technology, QR codes, Bluetooth and other technologies, but given very few merchants have the POS systems to accept these new types of technologies, consumers have not adopted. Currently, only 6.6 percent of merchants can accept NFC, and even less for QR codes or BLE technology, hence the extremely slow adoption rate. Simply put, the new solutions are NOT convenient, and do not replace consumers’ existing wallets, not even close.
It raises the risk of fraud. Fraud’s always a concern. However, since data isn’t stored on the device for Square and others, the data is stored on their servers, the risk is lessened. For example, there’s no need for you to fear one of your employees walking out with your tablet and downloading all of your customers’ info from the tablet. There’s also no heightened fraud risk for data loss if a tablet or mobile device is ever sold.
Mobile processing apps are error-free. Data corruption glitches do happen on wireless mobile devices. A merchant using mobile credit card processing apps needs to be more diligent to review their mobile processing transactions. Mobile technology is fantastic when it works.
Mobile wallets are about to happen. They aren’t about to happen, especially in developed markets like the U.S. It took 60 years to put in the banking infrastructure we have today and it will take years for mobile wallets to achieve critical mass here.
Setup is difficult and complicated. Setting up usually just involves downloading the vendor’s app and following the necessary steps to get the hardware and software up and running. The beauty of modern payment solutions is that like most mobile apps, they are built to be user-friendly and intuitive so merchants would have little trouble setting them up. Most mobile payment providers offer customer support as well, so you can always give them a call in the unlikely event that you have trouble setting up the system.
The biggest business opportunity in the mobile payments space is in developed markets. While most investments and activity in the Mobile Point of Sale space take place today in developed markets (North America and Western Europe), the largest opportunity is actually in emerging markets where most merchants are informal and by definition can’t get a merchant account to accept card payments. Credit and debit card penetration is higher in developed markets, but informal merchants account for the majority of payments volume in emerging markets and all those transactions are conducted in cash today.
Wireless devices are unreliable. Reliability is very often brought up as I think many businesses are wary of fully wireless setups. I think this is partly justified, but very easily mitigated, for example with a separate Wi-Fi network solely for point of sale and payments. With the right device, network equipment, software and card processor, reliability shouldn’t be an issue.
Posted in Best Practices for Merchants, Mobile Payments, Mobile Point of Sale, Smartphone Tagged with: (POS) systems, aggregators rates, apps, BLE technology, bluetooth, card, card processor, card reader, cash, cash register, chargebacks, consumer data, credit, credit card payments, credit card processing, credit card processors, credit card reader, credit-card, customer support, data, data loss, debit card, debit rate, device, fraud, fraud risk, hardware, industry experts, merchant account, Merchant's, mobile, mobile app, mobile credit card processing, Mobile Devices, Mobile Payments, mobile point of sale, Mobile processing apps, mobile processing transactions, mobile technology, mobile wallets, network, network equipment, nfc, nfc technology, payment solutions, payment technology, PayPal, phones, point of sale, qr codes, retailers, rewards cards, Security, Smartphones, software, Square, tablet, tablets, vendor's app, wallet providers, Wi-Fi network, wireless mobile, wireless mobile devices