January 7th, 2016 by Elma Jane
National Transaction is now offering Apple Pay to Canadian Merchants.
Apple Pay works with NTC’s EMV-contactless point of sale terminals in Canada.
Security and privacy is at the core of Apple Pay, and when a consumer adds a credit card to Apple’s mobile wallet, the actual card numbers are not stored on the device, or on Apple servers.
Apple Pay will create a unique Device Account Number that is assigned, encrypted and securely stored in the secure element on the device, the same way it operates in the U.S. Each transaction is authorized with a one-time unique dynamic security code.
To pay, consumers simply hold their mobile device near the contactless reader, exactly as they would a contactless card today. The payment information is then passed to the POS system once the consumer confirms the transaction using Touch ID on their device.
Bringing Apple Pay to NTC terminals addresses an increasing consumer demand for contactless payments, while also allowing Canadian businesses to offer customers the convenience of paying through an iPhone, iPad or Apple Watch.
American Express is Apple’s issuing partner in Canada.
Posted in Best Practices for Merchants Tagged with: Contactless card, contactless point of sale, contactless reader, credit card, EMV, merchants, mobile device, mobile wallet, payment, POS system, security code, terminals

October 15th, 2015 by Elma Jane
There are numbers of guidelines issued for accepting card payments, and merchants are expected to understand them all. To avoid issues down the road know a few basic rules in order to keep your business going without being penalized.
There’s a lot of ways to process a credit card: In-store, online, and by phone. There’s also different ways to pay and different brands of cards.
In-store and Card-not-present policies.
In-Store Policies:
- Always verify that the person presenting the card is the cardholder
- Ask for a 2nd ID for comparison
- Cards are non-transferable, cardholder MUST be present for purchase
- Compare the signature on the back of the card with that of the person who presents the card
- Inspect the card to confirm that it’s not visibly altered or mutilated
- Validate the card’s expiration date
Online/Phone Payment Policies: Card-not-present transactions
- Card account number
- Card billing address
- CID (3 digits on back of card OR 4 on the front)
- Card expiration date
- Card member’s home or billing telephone number
- Card member name (as it appears on the Card)
Rules for Visa, MasterCard and Amex that merchants need to know:
- Never store cardholder data on any systems to help minimize the risk of fraud and protect your business from potential chargebacks.
Complying with Federal Laws, State Laws and PCI
- A merchant should be familiar with and abide by Federal Laws regarding accepting credit cards. The Fair Credit Reporting Act is the federal law that establishes the foundation of consumer credit rights. This law regulates the collection and use of consumer credit information by merchants.
- Check state laws on the use of consumer credit information and accepting credit cards. Not all states have additional laws that regulate credit card practices, but some (such as California) prohibit merchants from requesting/requiring a customer to provide any personal information (like their address or telephone number) on any form involved with their credit card transaction. So, it is advised that merchants inquire about further information in their particular state.
- The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) is a set of requirements designed to ensure that all companies processing, storing, or transmitting credit card information uphold a secure environment. These rules essentially apply to any merchant that has a Merchant ID (MID). If you are a merchant that accepts credit card payments, you are required to comply with the PCI Data Security Standard, large or small businesses.
EMV Liability Shift Set By Visa and MasterCard as of October 1st
U.S. banks and credit card companies are now using the EMV (Europay, MasterCard, and Visa) technology. The EMV liability shift for fraud carried out in physical stores with counterfeit cards belongs to the merchant if it has not yet upgraded its POS system to accept EMV-enabled chip cards. While issuers absorb losses under card-network rules, that burden will shift to acquirers in cases where the fraud occurs at merchants unprepared for EMV.
It’s good to know every aspect of your business. The above guidelines are part of a business that every merchants should be familiar with. The main reason for these rules is to protect your business and keep your customer’s payment card data safe and secure.
To start accepting more credit cards give us a call now at 888-996-2273. We have the latest terminals that’s EMV/NFC capable.
Posted in Best Practices for Merchants, Credit Card Security, EMV EuroPay MasterCard Visa, Payment Card Industry PCI Security Tagged with: amex, card network, card payments, card-not-present, chargebacks, chip cards, credit card, credit card companies, Data Security Standard, EMV, EuroPay, MasterCard, merchants, MID, Payment Card Industry, PCI-DSS, POS system, U.S. banks, visa

October 1st, 2015 by Elma Jane
The day the payments industry has pointed to for several years arrives today, a turning point in the U.S.‘s migration to EMV chip-and-PIN cards.
Rules set by Visa and MasterCard as of today, the liability for fraud carried out in physical stores with counterfeit cards belongs to the merchant if it has not yet upgraded its POS system to accept EMV-enabled chip cards. Banks will be issuing EMV Chip Cards.
An enormous change, as everyone learns to deal with the new technology that requires consumers to insert their cards and leave them in the store machines throughout a payment transaction, rather than swipe.
In a recent survey, less than a third of merchants overall have invested in EMV-compliant technology, and one study said 80 percent of small and midsize merchants have not upgraded their systems as of today’s liability shift.
Issuers are claiming to be more prepared than merchants, but according to the Smart Card Alliance, around 200 million chip cards have been issued to U.S. cardholders. That, however, is less than 17 percent of the approximately 1.2 billion payment cards in circulation.
What is clear is that today does not represent the end of the journey. The lack of preparedness at the physical point of sale, however, may be beneficial for card-not-present merchants.
Over the past few months, the mainstream media has awoken to the fact that implementing EMV does not mean fraud will disappear. Fraudsters quickly adapted to the difficulty of counterfeiting cards by attacking Card-Not-Present channels, where a chip has no effect.
In other markets, fraud migrated quite rapidly to card-not-present channels. It is necessary on e-commerce merchants to protect themselves with an array of tools, like device authentication, one-time passwords, randomized PIN pad and biometrics. Fraud mitigation tools like data analytics, address and CVV verification, 3D secure and tokenization. These services should be available from their merchant acquirer processor or gateway.
There should be a gradual reduction in card fraud over the next 12-18 months in spite of the delays in this country’s EMV migration. It’s going to take time for the technology to be adopted.
U.S. Merchants’ overall relative lack of preparedness for EMV may give e-commerce and mobile merchants time they didn’t think they would have to explore the options.
Sophisticated authentication technologies such as biometrics will help increase the security of card transactions. Device-based verification could be easily incorporated in an EMV transaction.
Banks have expressed interest more in using the phone as a biometrics. It’s all going to depend on what is the most convenient way to access your funds. The nice thing about biometrics is it’s meant to enable more convenience and stronger security.
Posted in Best Practices for Merchants, e-commerce & m-commerce, EMV EuroPay MasterCard Visa, Mobile Payments, Mobile Point of Sale, Point of Sale Tagged with: banks, biometrics, card fraud, card-not-present, chip cards, chip-and-PIN cards, e-commerce, EMV, gateway, merchant acquirer, merchants, mobile merchants, payments industry, point of sale, POS system, processor, tokenization, Visa and MasterCard
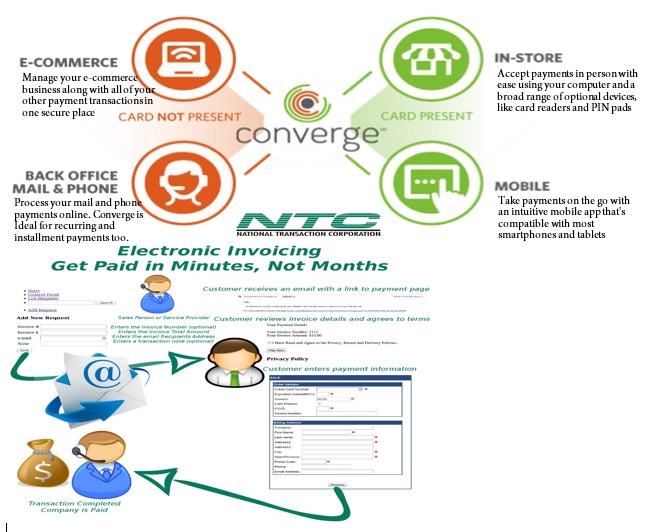
September 22nd, 2015 by Elma Jane
Virtual Merchant/Virtual Merchant Mobile now called Converge, is a popular product offering solutions for retail stores, Non Face to Face businesses along with E-commerce/Internet sites. Converege can be access anywhere with internet. Users can download the application on their smartphone or tablet. Converge also gives users the convenience of sending an invoice to customers electronically with NTC e-Pay!

For Retail store National Transaction offers the latest in EMV and NFC technologies. NTC customers can accept contactless payment with the same NFC technology used by Apple Pay, Google Wallet and SoftCard. NTC offers different solutions that cater to your business needs. For those already using a POS system, NTC integrates with most systems. NTC has you covered.

Posted in Best Practices for Merchants, e-commerce & m-commerce, Electronic Payments, Mobile Payments, Mobile Point of Sale Tagged with: Apple Pay, contactless payment, Converge, e-commerce, EMV, Google Wallet, nfc, POS system, smartphone, tablet, virtual merchant
August 27th, 2014 by Elma Jane
Backoff malware that has attacked point of sale systems at hundreds of businesses may accelerate adoption of EMV chip and PIN cards and two-factor authentication as merchants look for ways to soften the next attack. Chip and PIN are a big thing, because it greatly diminishes the value of the information that can be trapped by this malware, said Trustwave, a security company that estimates about 600 businesses have been victims of the new malware. The malware uses infected websites to infiltrate the computing devices that host point of sale systems or are used to make payments, such as PCs, tablets and smartphones. Merchants can install software that monitors their payments systems for intrusions, but the thing is you can’t just have anti-virus programs and think you are safe. Credit card data is particularly vulnerable because the malware can steal data directly from the magnetic stripe or keystrokes used to make card payments.
The point of sale system is low-hanging fruit because a lot of businesses don’t own their own POS system. They rent them, or a small business may hire a third party to implement their own point of sale system. The Payment Card Industry Security Standards Council issued new guidance this month to address security for outsourced digital payments. EMV-chip cards, which are designed to deter counterfeiting, would gut the value of any stolen data. With this magnetic stripe data, the crooks can clone the card and sell it on the black market. With chip and PIN, the data changes for each transaction, so each transaction is unique. Even if the malware grabs the data, there not a lot the crooks can do with it. The EMV transition in the U.S. has recently accelerated, driven in part by recent highprofile data breaches. Even with that momentum, the U.S. may still take longer than the card networks’ October 2015 deadline to fully shift to chip-card acceptance.
EMV does not by itself mitigate the threat of breaches. Two-factor authentication, or the use of a second channel or computing device to authorize a transaction, will likely share in the boost in investment stemming from data security concerns. The continued compromise of point of sale merchants through a variety of vectors, including malware such as Backoff, will motivate the implementation among merchants of stronger authentication to prevent unauthorized access to card data.
Backoff has garnered a lot of attention, including a warning from the U.S. government, but it’s not the only malware targeting payment card data. It is not the types of threats which are new, but rather the frequency with which they are occurring which has put merchants on their heels. There is also an acute need to educate small merchants on both the threats and respective mitigation techniques.. The heightened alert over data vulnerability should boost the card networks’ plans to replace account numbers with substitute tokens to protect digital payments. Tokens would not necessarily stop crooks from infiltrating point of sale systems, but like EMV technology, they would limit the value of the stolen data. There are two sides to the equation, the issuers and the merchants. To the extent we see both sides adopt tokenization, you will see fewer breaches and they will be less severe because the crooks will be getting a token instead of card data.
Posted in Best Practices for Merchants, Credit Card Security, Payment Card Industry PCI Security, Point of Sale Tagged with: access, account, account numbers, anti-virus programs, authentication, Backoff, card, card networks, chip, credit, Credit card data, credit-card, data, data breaches, devices, digital payments, EMV, magnetic stripe, Malware, Merchant's, Payment Card Industry, payments, PCs, PIN, PIN cards, point of sale, POS, POS system, programs, Security, security standards, Smartphones, software, system, tablets, tokenization, tokens, transaction, Trustwave, websites